August 12, 2022
Blockchain Layer 1 Vs Layer 2: What do you need to know?
Table of content
The importance of scaling in the blockchain ecosystem becomes more obvious as blockchain adoption grows rapidly. Thanks to the help of subtle improvements in the blockchain industry, this network can collect more apps and an increased number of transactions. With the growing attention to blockchain scaling, the question of what blockchain Layer 1 vs Layer 2 to choose is often a tricky task.
The growing volume of uses of cryptocurrencies has led to the development and adoption of blockchain layers with the goal of facilitating improved network protection and recordkeeping, alongside many other functionalities. Layer 1 is known as the base blockchain protocol. Layer 2 represents a third-party solution integrated with layer 1, allowing for better scalability.
This article will help you discover a detailed difference between layer 1 and layer 2 crypto.
Book a Free Call!
Learn more about our expertise and get a detailed approach and solution for your specific case
Book a callWhat Is Blockchain Scalability?
Blockchain technology offers a vast range of benefits, where most common are higher security, improved recordkeeping, and smooth almost immediate transactions. However, scalability is still a great concern, causing debates over whether layer 1 or layer 2 is best for new blockchain networks. Blockchain uses a decentralized system to perform transactions in several stages.
These steps and stages are required for hassle-free blockchain transactions that sometimes may need significant time and processing power. Let’s take as an example a blockchain network clogged with numerous transactions that are stacked one on top of the other. Here, the app won’t be able to fulfill all transaction requests from all users, causing a poor user experience. This is why blockchain scalability is essential for the successful future of blockchain networks.

What Are the Blockchain Layers?
Layer-0
Layer-0 works as a network architecture underlying the blockchain. It contains hardware, protocols, connections, and other key elements that create the foundation of a blockchain network. Being the foundation of the blockchain ecosystem, the Layer-0 layer is sometimes known as a “network of blockchains.” This layer also offers Inter-chain operability, allowing blockchains to communicate with each other. Layer-0 plays a key role in addressing future layer scalability difficulties, usually employing a native token to provide participation and development.
Layer-1
Layer-1 is essential, taking part in carrying out the vast range of tasks that create a blockchain network’s fundamental operations, including dispute resolution, consensus mechanism, protocols, languages, and restrictions. To be more specific, Layer-1 represents the actual blockchain. With the increasing number of individuals entering a blockchain, the computational power needed to add blocks to the network also grows rapidly, resulting in higher fees and longer processing times. The scalability issue seems to be improved by improved consensus techniques like proof-of-stake and the advent of sharding.
Layer-2
Blockchain requires more processing power to boost its productivity. However, it usually involves extra nodes, clogging the network. Even though involving new nodes is vital for sustaining a blockchain’s decentralized character, working with scalability, decentralization, or throughput will then affect other points on Layer-1.
This means that Layer 1 cannot be increased without relocating all essential processing to the second layer placed on top of the first, which is Layer 2. This became possible only due to allowing third-party solutions that are integrated with Layer-1. As a result, the new layer revamps the first, managing all the transactional validations. As you can expect, Layer-2 is placed on top of Layer-1 in the blockchain network and always exchanges data with it. However, now Layer-1 only manages adding and creating new blocks to the ecosystem.
Layer-3
The last one is Layer-3 which is also the only one visible to the human eye. This layer is the place where participants interact with the user interfaces (UI). However, it provides not only visibility but also utility in the form of intra- and inter-chain operability, like decentralized exchanges, liquidity provisioning, as well as staking apps. Decentralized apps (dApps) represent a type of Layer-3 interface that allows for real-world applications based on blockchain technology.
See Our NFT & Blockchain Development Process
Download this file to see how we helped our NFT clients, how we can lead you to success and what process we use to achieve this

Layer-1 Scaling Solutions
Currently, there are several options for the Layer-1 blockchain ecosystem that can boost throughput as well as overall network capacity. When blockchain uses Proof of Work, a transition to Proof of Stake can become an excellent option to increase transactions per second (TPS) and significantly reduce processing fees. However, there are still mixed views in the crypto world regarding the benefits and long-term uses of Proof of Stake.
Scaling solutions based on Layer 1 blockchain are usually offered by the project’s development team. Therefore, based on the solution, the blockchain community will require a hard fork or soft fork in the network. Larger changes, such as increasing the Bitcoin’s block size to 8MB, will always require a hard fork. Therefore, it will provide two versions of the blockchain, where one will be with the update and one without. The second option to boost a network’s throughput is sharding. This means splitting a blockchain’s operations into numerous smaller sections that will be able to process information simultaneously instead of sequentially.

Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
Layer 2 solutions lean on secondary networks that work independently and in parallel to the main chain.
Rollups
Zero-knowledge rollups are the most common types that combine off-chain Layer-2 transactions to then submit them as one transaction placed on the main chain. These systems act as proof of validity to verify the integrity of every transaction. Digital assets are saved on the original chain with the help of a bridging smart contract, where this smart contract is also responsible for confirming the rollup is functioning as needed.
Sidechains
Sidechains represent independent blockchain networks containing their own sets of validators. Therefore, the bridging smart contract placed on the main chain cannot check and verify the validity of the sidechain network. This means developers need to trust the sidechain is working the way it should as it’s capable of controlling assets on the original chain.
State Channels
State channels are a two-way communication environment between several transacting parties. The key task of these parties is to seal off a part of the underlying blockchain, connecting it to an off-chain transaction channel, which is done through a pre-agreed smart contract. When all transactions in the set are done, the final “state” of the channel is recorded to the blockchain for verification. This process helps boost the speed of transactions while also increasing the overall capacity of the network.
Nested Blockchains
Finally, a nested blockchain relies on a set of secondary chains that are placed on top of the main, also known as the “parent” blockchain. These systems work based on the rules and parameters provided by the parent chain. However, the parent chain won’t participate in executing transactions, only dispute resolution when required. Therefore, the whole work of these systems is done by the “child” chains that are responsible for returning the processed transactions to the main chain.
Layer-1 vs Layer-2 Comparison
Let’s explore the Layer 1 vs Layer 2 difference below:
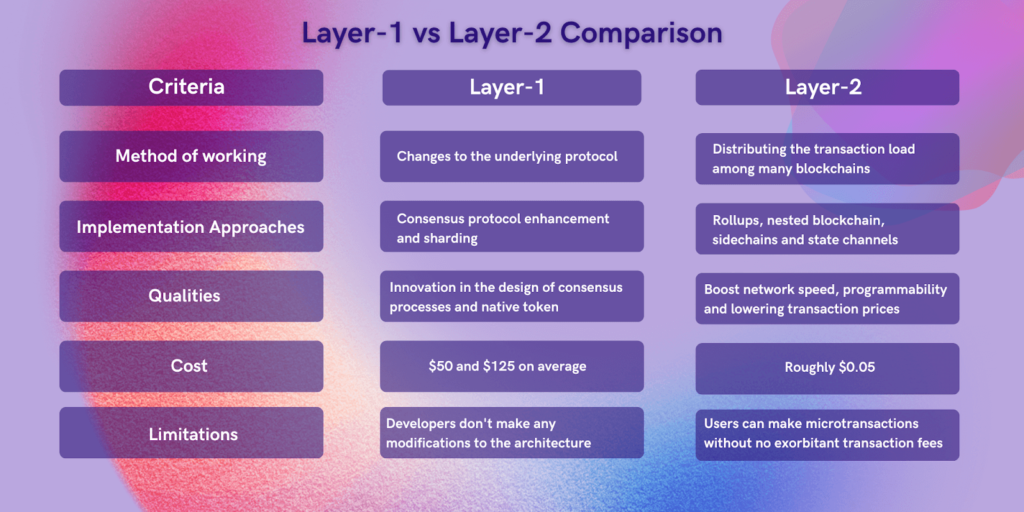
The Future of Scaling Blockchains
Scalability is one of the key factors preventing the blockchain sector from achieving widespread acceptance of cryptocurrencies in 2022. While the demand for crypto acceptance and use grows rapidly, the requirement to scale blockchain platforms also increases. Since both Layer-1 and Layer-2 levels have significant restrictions, the solution that will allow for scalability trilemma in the future is developing a protocol that will be able to overcome these constraints.
How Can Interexy Help?
Interexy is a trusted development partner with years of experience in blockchain. Given the fact that we are on the list of top Miami & Dubai Blockchain development companies in 2022, we provide top-notch blockchain application development services. Alongside the development of a vast range of software, we also offer team augmentation and consulting services.
Whether you need to know which layers to choose between L1 & L2, are looking for a trusted team to outsource your blockchain-based software development, or require help with overviewing your current project or smart contracts, we can help you.

Final Thoughts
Blockchain scalability is a popular concern that causes debate. Most of these debates relate to the question of what to choose between Layer 1 vs Layer 2 blockchain. In order to understand which layer suits your project and goals best, you should first explore the differences between them.
FAQs
What is a Layer 1 (L1) blockchain?
Layer 1 is the key blockchain network responsible for on-chain transactions.
What is a Layer 2 (L2) blockchain?
Layer 2 is the connected network responsible for off-chain transactions.
What is the difference between l1 vs l2 crypto?
Layer 1 refers to a blockchain architecture term for a network offering the infrastructure and consensus for Layer-2 projects to be built on top of it.