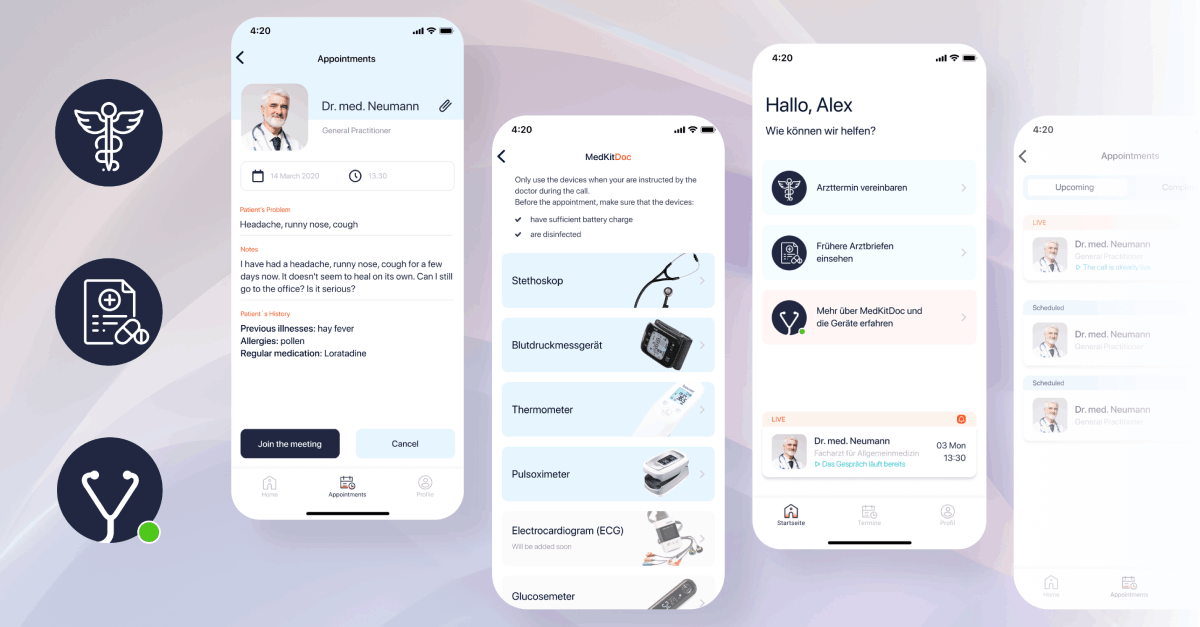
In the rapidly evolving healthcare technology landscape, ensuring the security and privacy of patient health data is paramount. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets forth stringent guidelines for protecting protected health information (PHI) and regulating the use of electronic health records (EHR). For developers of healthcare applications, compliance with HIPAA is a fundamental responsibility to safeguard patient confidentiality and trust.
 $309.93 billion
$309.93 billion
The global digital health market size was estimated at approximately $309.93 billion in 2023.
 $2.8 billion
$2.8 billion
The global healthcare compliance software market size was valued at $2.8 billion in 2022.
 $114.98 billion
$114.98 billion
The global telemedicine software market size was estimated at $114.98 billion in 2023.
The Basics of HIPAA Compliance
All healthcare providers, insurance companies, and enterprises dealing with sensitive patient data must strictly adhere to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Enacted in 1996 in the USA, HIPAA outlines the lawful use, management, and disclosure of protected health information (PHI). The violation of the Act may result in civil, monetary, or criminal penalties.
HIPAA compliance is mandatory for healthcare app development companies and is regulated by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the Office for Civil Rights (OCR). Many healthcare organizations still use outdated software and legacy systems that are no longer updated and robust enough to guarantee data protection. Therefore, developers use encryption to ensure the security and integrity of electronic protected information (ePHI).
Below, you can find the list of the main terms used when speaking about HIPAA compliance.
-
Individually identifiable health information (IIHI)
It’s a broader term than PHI, referring to information identifying individuals based on their demographics, health status, healthcare services received, and healthcare payments.
-
Protected health information (PHI)
Individually identifiable health information of an individual that was created, transmitted, and maintained by covered entities or their business associates.
There are 18 HIPAA identifiers, including names, phone numbers, social security numbers, account numbers, web URLs and IP addresses, photos, biometrics, etc.
-
Covered entities
Individuals, healthcare institutions, or organizations that transmit PHI electronically. These include health plans, healthcare providers, clinics, healthcare clearinghouses, and insurance companies.
-
Non-covered entity
Individuals, businesses, or agencies that aren’t health care providers.
-
Business associates
Individuals or organizations that deal with protected health information (use or disclose) on behalf of covered entities. These may be cloud service providers or healthcare app development companies processing patients’ data.
3 HIPAA Rules in App Development
1. The Privacy Rule
The Privacy Rule protects medical records and personal health information held by covered entities, setting strict limitations on using and disclosing the data without patient authorization. The rule safeguards health information in electronic, oral, or paper form, allowing individuals to access and correct their health records. In healthcare app development, this rule requires designing the features connected with data usage and disclosure with user consent in mind.
2. The Security Rule
The Security Rule applies to covered entities and business associates and secure storage, handling, and transmission of electronic patient health information (ePHI). The rule requires the implementation of administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to prevent data misuse and leaking and ensure its confidentiality and integrity. For healthcare mobile app developers, this rule means incorporating vulnerability assessment, access control, authorization, data encryption, and secure data transmission protocols.

3. The Breach Notification Rule
According to the Breach Notification Rule, covered entities and their business associates must notify patients, the Department of Health & Human Services (HHS), and the media about PHI breaches, regardless of their scope. Medical app developers must create mechanisms for prompt detecting and reporting of data breaches.

Explore our healthcare expertise and learn how Interexy can help you!
Let's talk6 Key Healthcare App Features that Need to be HIPAA Compliant
-
User Authentication and Access Controls
Healthcare apps should incorporate robust user authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to ensure that only authorized users can access patient information. Role-based access controls (RBAC) should be implemented to limit access based on user roles and responsibilities.
-
Secure Messaging and Communication
HIPAA-compliant healthcare apps must provide secure messaging capabilities to facilitate communication between medical care providers and patients. This includes end-to-end encryption of messages and secure transmission protocols to protect sensitive information.
-
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Management
Features related to electronic health records (EHR) management, such as viewing, updating, and sharing patient records, must comply with HIPAA regulations. Access to EHR data should be restricted to authorized personnel only, and audit trails should be maintained to track access and modifications.
-
Telehealth and Video Conferencing
Telehealth and videoconferencing software enable remote consultations between patients and healthcare providers. These features must utilize secure communication channels and encryption to protect the confidentiality of patient health data transmitted during virtual visits.
-
Patient Consent and Authorization
Features that involve collecting patient consent and authorization for data processing or sharing must comply with HIPAA requirements. This includes providing clear explanations of data usage and obtaining explicit consent from patients before accessing or sharing their information.
-
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Healthcare apps should incorporate robust data backup and disaster recovery features to ensure the integrity and availability of patient data. Data backups should be encrypted and stored securely to prevent data loss or unauthorized access.
Consult our HIPAA consultants to learn how to make your app compliant!
Get in touchA Checklist for Building a HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare App
-
Understand HIPAA Regulations
Before diving into development, familiarize yourself with the key provisions of HIPAA, especially the Privacy Rule and the Security Rule. The Privacy Rule outlines standards for protecting individually identifiable health information, while the Security Rule specifies the technical and physical safeguards required to secure electronic protected health information (ePHI). If needed, turn to a healthcare IT consulting services company.
-
Implement Strong Access Controls
Ensure that your healthcare application incorporates robust authentication and authorization mechanisms. Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to restrict access to electronic protected health information (ePHI) based on user roles and responsibilities.
-
Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Utilize strong encryption methods to protect ePHI both when it is stored (at rest) and when it is transmitted over networks (in transit). Use industry-standard protocols such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) for data transmission.
-
Maintain Data Integrity
Implement measures to ensure the integrity of ePHI. This involves mechanisms to detect and prevent unauthorized alterations to data, such as using hashing techniques and digital signatures.
-
Perform Regular Security Risk Assessments
Conduct ongoing risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities in your healthcare app and infrastructure. Address any identified risks promptly to mitigate security threats.
-
Adopt Secure Software Development Practices
Follow secure coding practices and conduct regular healthcare security testing throughout the development lifecycle. Implementing secure development methodologies can help prevent common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS).
-
Establish Data Backup and Recovery Procedures
Implement reliable data backup procedures to protect electronic health information against data loss or corruption. Test data recovery processes periodically to verify their effectiveness.
-
Implement Audit Controls
Enable audit logging to track access and modifications to ePHI within your healthcare application. Maintain audit trails to facilitate forensic analysis and compliance audits.
-
Train Staff on HIPAA Compliance
Educate all personnel involved in developing, deploying, and maintaining the healthcare app about HIPAA regulations and best practices. Ensure that everyone understands their responsibilities for safeguarding ePHI and penalties for non-compliance.
-
Execute Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
If your medical app interacts with third-party service providers (business associates) that handle ePHI, execute Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with them. A BAA establishes each party’s responsibilities regarding HIPAA compliance.
Interexy’s Experience in HIPAA Development
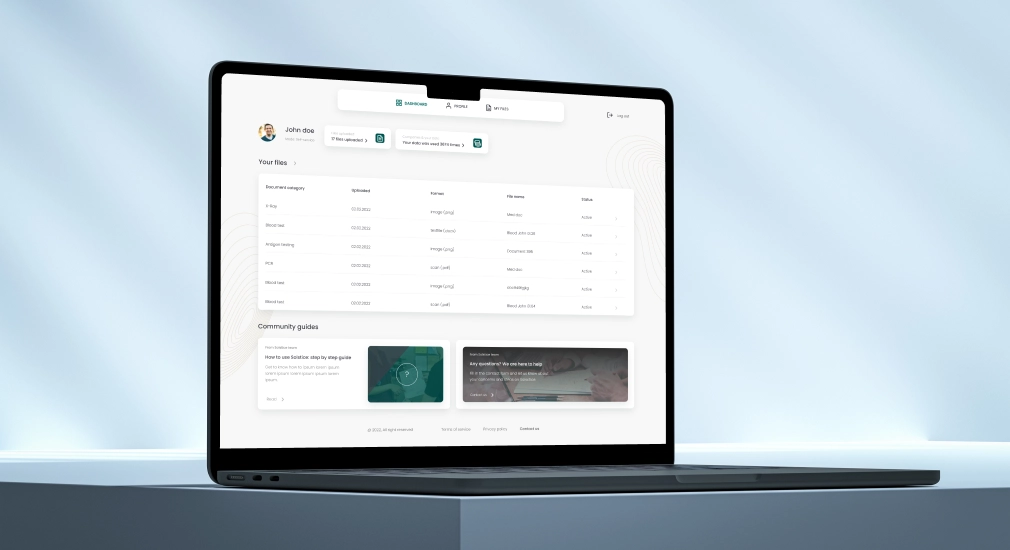
Solstice is a groundbreaking healthcare marketplace platform developed by Interexy to securely manage sensitive patient data like genome analyses, X-rays, and health records. Focused on patient data ownership and innovation, the platform enables therapeutic organizations to access comprehensive health information while adhering to HIPAA compliance.
Interexy implemented advanced encryption, including twice-encrypted data and a three-key system to meet strict HIPAA standards. By delivering a HIPAA-compliant MVP with smart filters and user-friendly design, Interexy ensured Solstice is both secure and scalable, paving the way for investment and innovation in the healthcare sector.
HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare App Development by Interexy
HIPAA App Development FAQs
-
What is HIPAA compliance in software development?
HIPAA compliance in software development ensures that applications handling Protected Health Information (PHI) meet stringent standards for data privacy, security, and confidentiality. A HIPAA-compliant app developer must implement safeguards like data encryption, secure user authentication, and audit logging to protect sensitive health data. This is crucial for businesses investing in HIPAA app development to avoid breaches and legal penalties.
-
What data is subject to HIPAA?
Protected Health Information (PHI), subject to HIPAA regulations, includes any data that identifies an individual’s health status, healthcare services received, or payment for healthcare. This encompasses medical records, lab results, appointment details, and health insurance information. When engaging in HIPAA-compliant app development, developers must ensure all PHI is securely stored and transmitted, especially when creating applications like telemedicine platforms or patient portals.
-
Which healthcare apps need to comply with HIPAA regulations?
Any healthcare app that handles PHI must comply with HIPAA regulations to protect patient privacy and data security. This includes HIPAA-compliant mobile app development for electronic health record (EHR) systems, telemedicine platforms, patient portals, and health data tracking apps. Businesses aiming to build a HIPAA-compliant app or use a HIPAA-compliant app builder must prioritize robust security measures during development.
-
What is required to be HIPAA-compliant?
To be HIPAA-compliant, healthcare apps must meet key requirements, including safeguarding PHI with encryption, secure access controls, and routine audits. Development teams must follow best practices in HIPAA-compliant mobile app development to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Companies also need to maintain updated policies and documentation to demonstrate compliance during audits.
-
What are the consequences of non-compliance with HIPAA regulations?
Non-compliance with HIPAA can result in severe financial penalties, legal actions, reputational damage, and loss of trust. For companies investing in HIPAA compliance application development, adhering to these regulations minimizes risks while fostering credibility in the healthcare industry. HIPAA-compliant app development ensures patient data protection and avoids costly corrective actions that can disrupt operations.