Web 3.0, also known as Web3, is a buzzword in modern development. As a possible future version of the internet based on public blockchains, Web 3.0 represents a record-keeping system well-recognized for facilitating various cryptocurrency transactions.
What is Web3? It is a decentralized phenomenon. Therefore, individuals can own and govern sections of the internet rather than access it through services provided by larger companies like Google, Apple, and Facebook.
Web 3.0 also doesn’t require “permission,” meaning that authorities won’t have to decide whether someone gets access to services. No “trust” is also required, meaning an intermediary isn’t essentially needed for virtual transactions between two or more parties.
Since these agencies and intermediaries are collecting most of the data, Web 3.0 will protect user privacy and ensure higher protection. Decentralized finance, known as DeFi, refers to a component of Web 3.0 gaining popularity.
It enables real-world financial transactions based on the blockchain ledger without any need for banks, governments, or third parties. We carefully curated this overview to discuss Web 3.0 technology today to help you learn more about Internet 3.0, how it works, and its uses today and in the future.
Key Statistics
The market size of Web 3.0 technology was valued at $2.25 billion in the year 2023.
The market for Web 3.0 is forecast to increase by a 43.7% CAGR from 2023 to 2030.
The market size of Web 3.0 technology is projected to reach $33.53 billion in 2030.
Web 3.0 Meaning and Identity
Answering a few key questions will be enough to understand the essence of this phenomenon:
What is Web 3.0? It is the next iteration of the World Wide Web, focusing on creating a decentralized platform. Web 3.0 is also called Web3 and processes information in an intelligent, human-like way due to semantic technologies utilization.
What are Web 3.0 technologies? Web3’s identity lies in using technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), semantic Web, and blockchain. Web3 relies on them to provide higher transparency while ensuring a fast and more personalized user experience.
What are Web 3.0 examples? Leading tech companies are investing in Web 3.0 solutions, with Facebook and Apple standing out as the most prominent examples. Although Apple’s stance on blockchain and Web 3.0 has changed multiple times, the company ultimately eased its policy and is now more open to adopting these innovative technologies.
In an original version, Web 3.0 was called the Semantic Web, delivered by Tim Berners-Lee, who also invented the World Wide Web. He delivered this technology to build the next internet, which should be more intelligent, trusted, open, and autonomous than its predecessor.
However, today’s Web 3.0 meaning has changed due to many reasons. Now, this technology focuses on giving control of the data back to consumers. Therefore, instead of using platforms and providing their data in exchange, consumers can participate in the governance of all these tech platforms. For example, users can sell their data to advertisers on the Web but still have all rights and ownership.

How does Web 3.0 Work?
Being aware of the Web 3.0 definition and the benefits Web 3.0 will offer, it will become more engaging to know how exactly this technology works. As we mentioned above, Web3 works on the blockchain. Therefore, all the technology’s benefits also relate to what blockchain offers.
Let’s first go through the definition of blockchain. Simply put, a blockchain represents a digital chain of data blocks that form a vast system that cannot be deleted, changed, or hacked. Every time this block of digital information is created, it links to the previous block in the chain. The process continues whenever blocks are created.
Blockchain is a digital record of information that can be distributed but not edited or deleted. Therefore, there is no centralized system of control placed on the blockchain. This guarantees the security and privacy of our information.
Since blockchain is decentralized, it offers the basis for the development and growth of Web 3.0. Integrating AI, ML, and IoT into Web 2.0 while using blockchain, a new version known as Web 3.0 hopes to provide a significantly different user experience highly tailored to needs.
Still have questions? We have a great expertise in Web3 development and our consultants are ready to help with a variety of tasks.
Get in touchThe Evolution of the Web

What is Web 1.0?
Web 1.0 is the earliest version of the Internet, also known as Web1 or Syntactic Web. Web 1.0 has been available only for reading. Most users were content consumers, while the makers were engineers who usually built websites delivering content primarily in text or graphic format. Web 1.0 was produced in 1991 and existed till 2004.
What is Web 2.0?
We have probably seen the Web in its current version, Web 2.0, estimated as the interactive read-write and social web. The key is that you don’t always need coding skills to participate in the creation process in the Web 2.0 universe. Many modern applications have been created so that almost everyone can become a creator.
Web 2.0 allows users to share their thoughts, create videos, and make them freely available to millions of others to watch, comment on, and interact with. For example, YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and other social media sites are great examples of Web 2.0 applications.
Companies who want to develop new ideas and go with more Social Web use technologies like HTML5 and CSS3. Some Javascript frameworks, including React, Angular, VueJs, and others, are used for this purpose. Therefore, developers must create a mechanism to enable and engage users since Web 2.0 is built around them.
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0, also called Semantic Web or read-write-execute, is the last version that has existed since 2010 and allows for the Web’s future. Since Web 3.0 uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), the new version helps computers easily analyze data. This aids intelligent generation and distributes relevant content according to a user’s needs, offering a highly tailored user experience.
Even though there are several differences between all these versions, decentralization is the key in all of them. Today’s developers working with Web 3.0 rarely develop and deploy applications that run on a single server or store data in a common database.
Most modern Web 3.0 applications are crafted on blockchains, representing a decentralized network of numerous peer-to-peer nodes (servers). These programs also got the name programs are known as decentralized apps (or shortly DApps), which are highly popular in the Web 3.0 community.
Building a Decentralized Application (DApp) requires a deep understanding of blockchain technology programming languages such as Solidity. The process involves:
- Creating smart contracts;
- Deploying them to the blockchain;
- Ensuring they function correctly in a decentralized network.
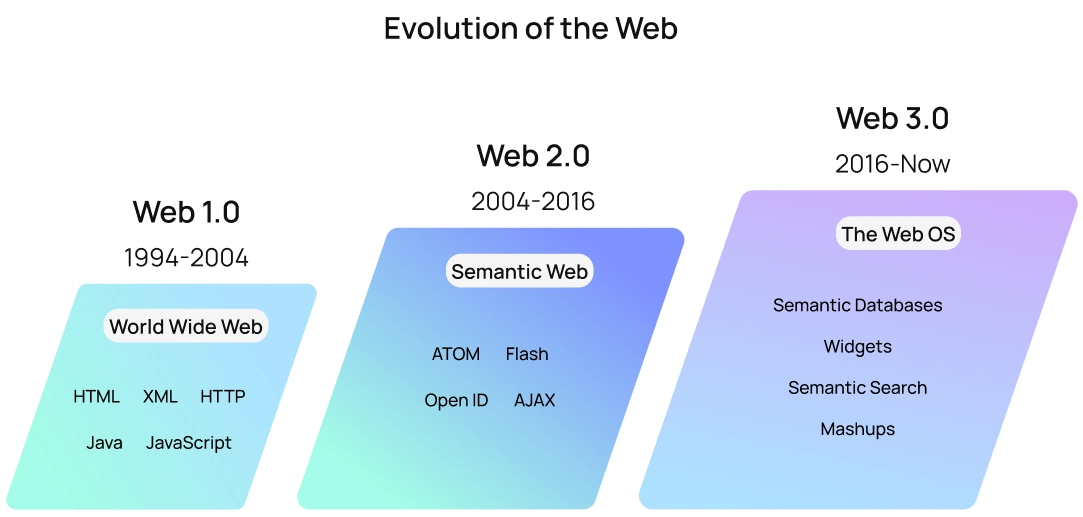
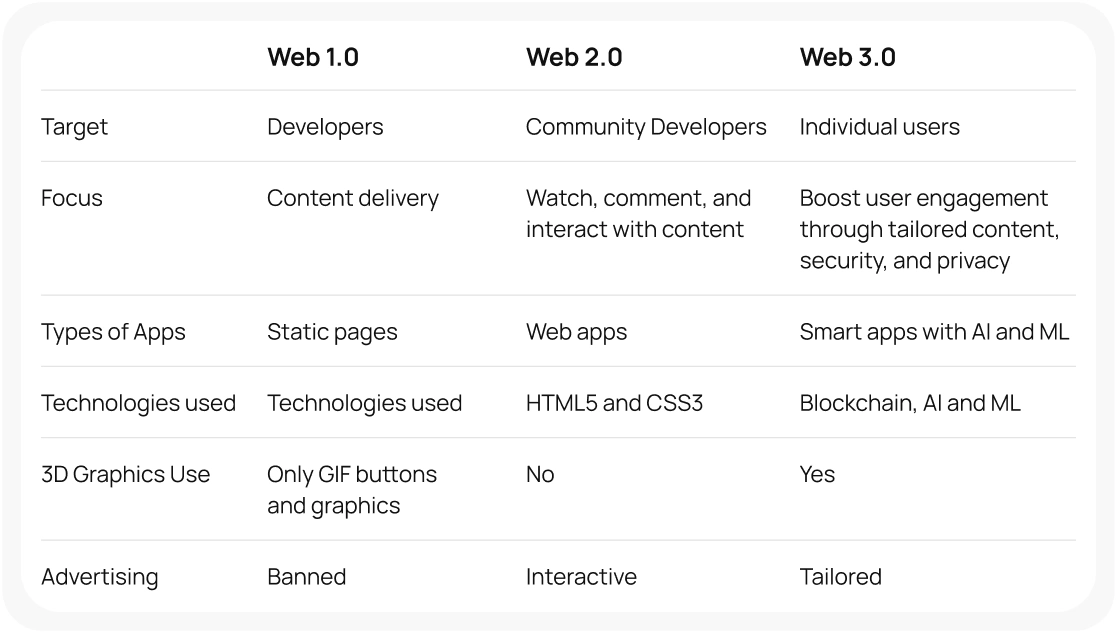
Below you will see key differences between all three versions:
What are the Advantages Of Web 3.0?
-
Ownership of Data and Information
With Web 3.0, users will gain complete ownership and control of their data or information with the security of encryption. These data can be shared only with permission, need, or/on a case-by-case basis.
Today, market giants like Facebook and Amazon have many servers that store personal information regarding income, dietary preferences, and credit card information. This data is collected to provide better and more user-oriented services and sold to the marketers who pay millions every year for this.
-
Easy Access to Information
One of the key benefits of Web 3.0 is the ability of users to access data from anywhere, primarily driven by the immense smartphone and cloud use worldwide. The goal is to guarantee consumers have the easiest possible access to information regardless of where they are.
-
No Need in Central Point of Control
The blockchain leader offers an all-in-one trusted platform where all data is encrypted while the applications are unbreakable. Therefore, there is no need for intermediaries. No government or third parties will be able to kill sites or servers, and no one will be able to control the identities of others.
-
Uninterrupted Service
The suspension of accounts and denial of distributed services with Web 3.0 are reduced dramatically. This is because there is no single point of failure; the disruption of the server will be a bare minimum. All data is stored on the distributed nodes to ensure redundancy, while multiple backups will prevent a seizure or server failure.
What are the Disadvantages Of Web 3.0?
-
Ownership Concerns
Even though Web 3.0 is popular, it is still developing, and not everything can be realized. For example, experts believe that regular consumers won’t be able to have ownership of Web 3.0 projects as everyone expects. It seems that only venture capitalists and investors will own them.
-
Tough to Regulate
Some experts also think decentralization may complicate monitoring and regulating Web 3.0. Therefore, it may lead to increased hacker attacks, cybercrimes, online abuse, and more.
-
Surfing Web 3.0 Requires Better Processors
Outdated devices won’t be able to handle Web 3.0. It means people will require new devices with above-average specifications to provide hassle-free use of the new version of the internet.
Disadvantages are not a verdict
Web 3.0 Use in Real Life
Apple Siri
All Apple’s device owners are already familiar with Web 3.0. Siri, which exists on any Apple device, represents an intelligent Web 3.0 app. This app also shows how much Web 3.0 is maturing. Even though Siri previously often answered with “I don’t know,” now it can answer almost any question.
Wolfram Alpha
Wolfram Alpha represents a great combination of AI and machine learning on distributed systems. It operates with numerous computers to analyze information and respond to inquiries relevantly. When a user inputs an item, like an apple, he will get a wealth of data, such as nutritional information.
Facebook is also one of the greatest voices in Web 3.0. It has been updated by putting a huge amount of development focusing on the metaverse in media and entertainment. The existing APIs make it much easier for engineers in and outside Facebook to update existing communities into Web 3.0 spaces.
Uniswap
Uniswap is one of the famous Web 3.0 applications examples of DeFi in the Web 3.0 ecosystem. A decentralized exchange (DEX) operates on the Ethereum blockchain. Uniswap allows users to swap various cryptocurrencies without needing a traditional centralized exchange. The platform uses smart contracts to facilitate secure, peer-to-peer transactions directly on the blockchain.

Web 3.0, Crypto and Blockchain
We may often face the “What is web 3.0 crypto and blockchain?” question. Let’s learn how these terms are interconnected with each other.
As mentioned above, Web 3.0 apps and websites will heavily rely on blockchain and blockchain entities like non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and crypto. Web 3.0 tokens are usually associated with the vision of creating a new version of a decentralized internet.
By using Web 3.0 tokens, people can create control and contribute to various projects. For instance, Reddit refers to creating a mechanism that will make cryptocurrency tokens freely available to consumers to control elements of the on-site communities.
Therefore, blockchain will be the key driver of Web 3.0 and create multiple Web 3.0 blockchain apps. It will also guarantee security, encryption, and a user-centric network that provides users complete control and ownership over their information.
How is Web3 Related to NFTs?
Web3 and NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are related concepts in blockchain and decentralized applications. It represents the next generation of the blockchain-based internet and aims to replace centralized structures with decentralized networks for greater user control over their data and interactions. On the other hand, NFTs are unique digital assets that use blockchain to prove ownership and authenticity.
They can represent digital art, music, virtual real estate, and more. Web3 and NFTs share similarities regarding proof of ownership and authenticity of digital assets, use of decentralized structures, potential for new economic models for creators, and interoperability between different blockchain platforms. They are both crucial components of the digital economy, providing users with greater control and new opportunities.
Why Web 3.0 Is Important for the Future
Web 3.0 is still in its infancy, making it questionable whether it will be important for the future and whether or not it is worth investing in. However, one thing is obvious: businesses should pay close attention to this new version of the Internet as it will bring many benefits to businesses and people in the coming years.
Experts believe that Web3 in banking will tremendously impact the finance industry and asset management. For instance, rather than using a centralized bank, people can access a global suite of financial products by allowing services to interact directly with their digital wallets.
It is also clear that Web 3.0 will boost the use of NFTs and digital assets, allowing users to monetize their skills in brand-new and engaging ways providing businesses with multiple investment opportunities.
“What is Web 3.0 and metaverse?” is a critical inquiry for future advancement. Web 3.0 and metaverse are interrelated. Web 3.0’s decentralized, blockchain-driven Internet provides the underlying technology to support the metaverse’s vast, interconnected virtual spaces.
Integrating cryptocurrencies and NFTs in Web 3.0 is also vital for the digital economy within the metaverse. In essence, while Web 3.0 reshapes the infrastructure and operations of the Internet, the metaverse expands on how we perceive and interact with digital spaces, making them more immersive and lifelike.

AI/Machine Learning Web 3.0 Products
-
Decentralized AI Marketplaces
These platforms leverage blockchain’s immutable ledger and smart contract capabilities to facilitate the secure trading of AI models and datasets. They might use advanced cryptographic techniques like homomorphic encryption to protect the intellectual property of AI models while still allowing for their evaluation.
-
AI-Enhanced Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, encoded with complex AI algorithms, can execute transactions based on multi-dimensional data analysis and predictions. These contracts might integrate neural network-based models to make real-time decisions, adapting to market dynamics or user behaviors in applications like automated insurance claims or dynamic pricing in DeFi protocols.
-
Predictive Analytics in DeFi
Advanced machine learning models, such as deep learning or reinforcement learning, are employed to analyze vast arrays of decentralized financial data. These models predict market trends and token performance, utilizing techniques like sentiment analysis on blockchain data and social media and time-series forecasting for cryptocurrency prices.
-
Personalized NFTs with AI
This involves generative adversarial networks (GANs) or other generative AI models to create unique, evolving NFTs. These NFTs could change in response to environmental factors, user interactions, or external data feeds, leading to dynamic digital art or game assets that offer unique, personalized experiences.
-
Decentralized Data Lakes for AI Training
Platforms are being developed where individuals can contribute their data to a decentralized storage solution, often built on blockchain or distributed ledger technologies. This data can be anonymized and aggregated to train machine learning models, with contributors compensated via cryptocurrency.
-
AI Moderation in Decentralized Networks
Implementing sophisticated natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision algorithms to autonomously moderate content on decentralized platforms. These AI systems must be designed to respect the decentralized ethos, possibly using federated learning to improve models without centralizing data.
-
Blockchain-based AI Model Verification
Blockchain technology creates an immutable record of AI model development, including training data, model parameters, and changes over time. This is particularly important in fields requiring high trust and transparency, such as healthcare diagnostics or financial forecasting models.
-
Tokenized AI Computer Sharing
This involves creating decentralized networks where individuals can contribute their computational resources (like GPU time) to AI processing tasks. Blockchain technology tracks contributions and distributes rewards, often as tokens. This approach can democratize access to expensive AI computations, enabling broader participation in AI research and development.
-
Privacy-preserving AI Analytics
Integrating advanced machine learning with cryptographic techniques like zero-knowledge proofs or secure multi-party computation allows for analyzing sensitive data (such as medical records or financial transactions) without exposing individual data points, ensuring privacy compliance and data security.
-
AI-driven DAOs
These decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) integrate AI algorithms to aid governance decisions. They might use predictive models to forecast the outcomes of certain governance decisions or automate routine organizational tasks based on learned patterns and rules, reducing the administrative burden on human participants.
How to Get Your Brand Ready for the Web 3.0 Revolution?
We have answered , “What does Web3 mean?”. So, It’s time to explore the measures to help businesses stay on the cutting edge of technological development.
-
In-depth Understanding of Web 3.0 Technologies
Deeply study blockchain protocols, consensus mechanisms, smart contracts, DeFi, NFTs, and DAOs. Analyze case studies of blockchain integration in various sectors to understand its impact on operational efficiency, data integrity, and customer trust.
-
Advanced Digital Strategy Adaptation
Conduct a thorough SWOT analysis of how blockchain, AI, and IoT could disrupt your industry. Develop a phased strategy for integrating smart contracts into your supply chain or customer interactions.
-
Strategic Investments in Cutting-edge Technologies
Explore investments in blockchain infrastructure, decentralized data storage solutions, and AI-driven analytics tools. Collaborate with tech startups or established blockchain platforms for pilot projects, monitoring scalability and interoperability issues.
-
Integrating Decentralization into Business Operations
Experiment with decentralized organizational structures, perhaps starting with a subsidiary or a new product line. Evaluate the feasibility of migrating certain business processes or data storage to distributed ledgers.
-
Sophisticated Approach to Digital Identity and Privacy
Implement Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) solutions to give users control over their data. Update your cybersecurity framework to address the unique challenges of decentralized data management.
-
Advanced AI and Machine Learning Integration
Develop AI models for predictive customer behavior analysis, market trend forecasting, and personalized content delivery. Implement machine learning algorithms for real-time fraud detection and automated customer service enhancements.
-
Comprehensive Education Programs for Teams and Customers
Develop in-depth training modules for your team on blockchain technology, cryptographic security, and regulatory compliance. Create customer education campaigns that detail the benefits and practical applications of Web 3.0 in your services.
-
Developing a Community-сentric Brand
Utilize advanced social listening tools to gauge community sentiment and feedback. Engage in transparent communication practices, possibly using blockchain for verifiable community polls or feedback mechanisms.
-
Proactive and Informed Strategic Agility
Web3 development company can help to establish a dedicated R&D team to monitor Web 3.0 trends and propose adaptive strategies. Incorporate scenario planning to anticipate and prepare for future Web 3.0 technology adoption states.
-
Input headingEnhanced Security and Compliance Frameworks
Invest in next-gen cybersecurity solutions like quantum-resistant encryption for protecting blockchain transactions. Engage with legal experts to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape of digital assets and decentralized finance.
-
Exploring Advanced VR and AR Applications
Develop or partner for immersive VR/AR experiences integrating with blockchain for verifiable, interactive digital assets. Explore AR applications for enhancing physical products with digital experiences, possibly linked with Web 3.0 NFT.
-
Innovative Tokenization Strategies
Research token economics (tokenomics) to design a tokenization strategy that adds value to your customers. Consider creating a branded cryptocurrency or utility tokens that can be used within an ecosystem of products and services.
How Can Interexy Help?
Being on the list of top Dubai and Miami Blockchain development companies in 2022, Interexy always tracks the latest technologies from the inside to boost the industry’s standards. We have in-depth experience in blockchain app development services, providing projects with highly skilled and specialized resources.
We crafted a GameDay – a unique web application developed from scratch. It is a sports platform with marketplace elements, which allows users to stay informed about the latest sports matches, make bets, watch matches, post something, and earn NFTs just for using the platform.
Alongside NFT creation, NFT marketplace development, smart contract audit, and blockchain development, we also provide outstanding crypto development services. Being the leader in this niche, we work with larger, well-known companies and people, like American rappers Lil Durk and Sandbox.
Bottom Line

We bet you have heard of Web 3.0 and blockchain somewhere. But we also bet you didn’t fully understand what this technology represents and why all this buzz around it happens. This overview contains all the needed information regarding Web 3.0 and shows why you should invest your attention.
Let’s book a free call to talk with our experts about your idea!
Book a callFAQs
-
What is Web 3.0 in simple words?
Web 3.0, in simple terms, is the next generation of the Internet, which focuses on decentralization, increased user privacy, and more intelligent web interactions. Web 3.0 will bring users more control over their data using blockchain technology.
This means that instead of storing your information on central servers owned by big companies, it’s spread out across a network, making it more secure and less controlled by any single entity.
Additionally, Web 3.0 uses advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to make a more personalized and efficient online experience, where the Internet understands and anticipates what you are looking for more sophisticatedly.
-
What is another name for Web 3.0?
The “Semantic Web” is Another name for Web 3.0, and Tim Berners-Leeinventor coined this term. The idea behind the Semantic Web is to create a more intelligent and intuitive network where data is interconnected meaningfully that humans and machines understand.
In the Semantic Web, information is structured and tagged so that computers can read it directly, allowing them to process, analyze, and generate information based on user needs effectively.
This concept is closely related to the principles of Web 3.0, which emphasize enhanced usability, AI integration, and decentralized data management.
-
What is a component of Web 3.0 that describes things in a way that computers can understand?
Semantic technology is at the core of the Semantic Web (a term often used interchangeably with Web 3.0). It involves using standards, languages, and frameworks that enable computers to interpret and understand the meaning or context of words on a web page rather than just parsing keywords.
This technology often employs:
- RDF (Resource Description Framework): A standard model for data interchange on the web.
- OWL (Web Ontology Language): A language for defining and instantiating Web ontologies.
- SPARQL (SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language): A query language and protocol for retrieving and manipulating data stored in RDF format.
-
What is the difference between metaverse and Web 3.0?
The metaverse is built upon technologies like VR, AR, and 3D modeling and aims to create an immersive, lifelike virtual experience, whereas Web 3.0 is built on blockchain, AI, and machine learning and aims to make the Internet more intelligent and efficient.
The metaverse is focused on creating new virtual environments and experiences, while Web 3.0 is focused on changing how data is handled and interacted with across the Internet.